Increasing aesthetic concerns makes the dental composite one of the ideal materials for dental restorations. The tooth color material has good strength and color stability. It is easy to manipulate and required a specific curing wavelength. The most common use wavelength in curing light ranges between 450-480 nm. The curing light falls under the blue spectrum light. Adequate curing depth and intensity are required for flawless restoration. There is various curing light available on market. The selection of the best dental composite curing light is very critical and essential. There are some Parameters that can help the dentist to find the best curing light for a dental clinic. Let’s discuss some important aspects that will help to find the best curing light.
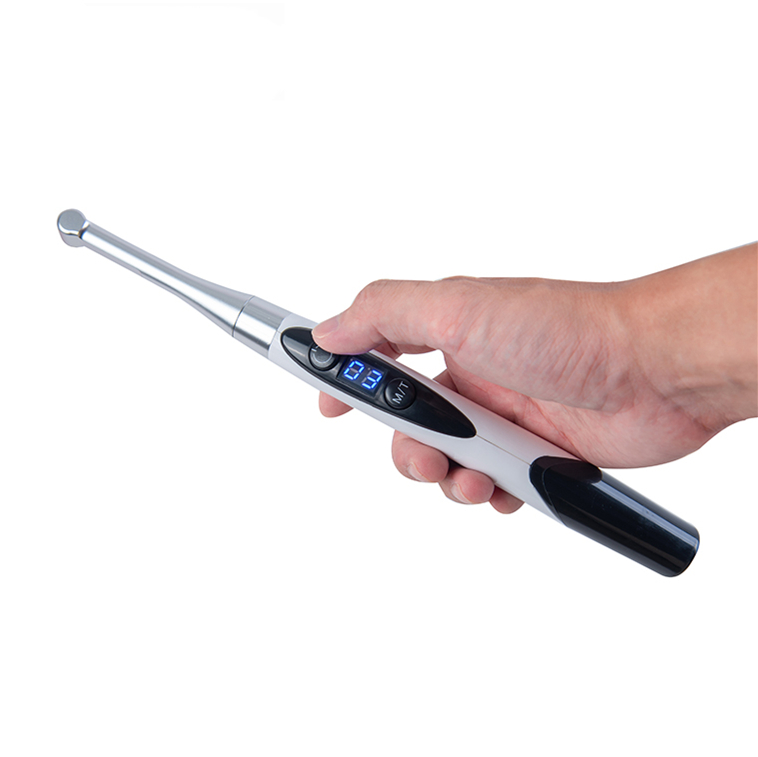

Correct wavelength:
Dental procedures are very sensitive and required a unique set of armamentariums. The wavelength of curing light changes with the procedure type. Dental composite restorations are the most common procedure in dentistry. They required a curing wavelength of above 450 nm. The curing light of a higher wavelength produces more heat and wastes energy. The higher wavelength can’t fasten the rate of curing, rather than create reduce the quality of final restoration.
Battery Life:
Mostly curing lights are chargeable. Some have output battery devices. The best curing light should have a long output time and storage ability. It eliminates clinical flaws and ensures the best dental restoration. The batteries that are only chargeable by the manufacturer should be avoided. They give more cost and are not economical for the operator.
Compatible with initiator:
Initiators are chemical compounds used to control the reaction. Chemical cured dental composites don’t require curing light but they are difficult to handle and have a long curing time. On the other hand, the photoinitiator used the light of a specific wavelength and carry the chemical reaction. The most commonly used photoinitiations in dental resin are camphor quinone, iodonium salts and electron donors. The curing light or blue light generates the free electrons and radical exchange leads the curing process.
Digital Display:
The digital display helps the operation to evaluate the curing time and set the wavelength. A clear display is making the curing fast and accurate. Polymerization of resin required 20-30 seconds, depending upon the type of composite used.
Easy to Sterilized or disinfect:
Cross infection is the process of the spread of infection in a clinical step. To avoid the unnecessary spread of infection, sterilization and disinfection are necessary. The operator should choose the curing light that can be sterilized without any changes in the material.
Durable and Economical:
Durability and cost are important factors in the selection of curing light. The long-term utilization can damage the instrument or reduce the curing power.
Warranted:
The warranted tools are more reliable and cost-effective. Select the curing light that has some warranty and can be replaced in case of any internal system defect.
Parts of curing light system:
The curing light system consists of following components;
- Handle.
- Nose cone.
- Eyeshield.
- Digital screen.
- Time and power button
- Power module
The handle of the curing light enhances the grip on the instrument. The nose cone guides the light pathway to the substrate. Blue curing light can affect the eyes of the operator. The eyeshield protects against the effect of damage. The curing light also has a digital screen to display the time of curing. The rechargeable light has a power module for the recharging setup.
Types of curing light:
- Quartz-tungsten-halogen.
- Light-emitting diode
- Plasma arc curing
- Argon laser units
Quartz-tungsten-halogen.
The curing light emits ultraviolet irradiation and visible light that keeps the wavelength limit between 400 and 500 nm with minimum heat production. The light intensity of Quartz-tungsten-halogen ranges from 400 to 1200 mW/cm2.
Light-emitting diode
LED light-curing devices emit light in the visible blue spectrum between 440 and 490 nm and do not produce heat. As a result, LED devices don’t need filters.
Plasma arc curing
PAC light-curing units contain a xenon gas that is ionized to produce plasma. The high-intensity white light emitted is filtered to minimize heat and to limit the output to the violet-blue part of the visible spectrum (400–500 nm).
Argon laser units
Visible light-activated dental materials contain an initiator such as camphor quinone (CQ) that absorbs light at the appropriate wavelength (approximately 470 nm for CQ).